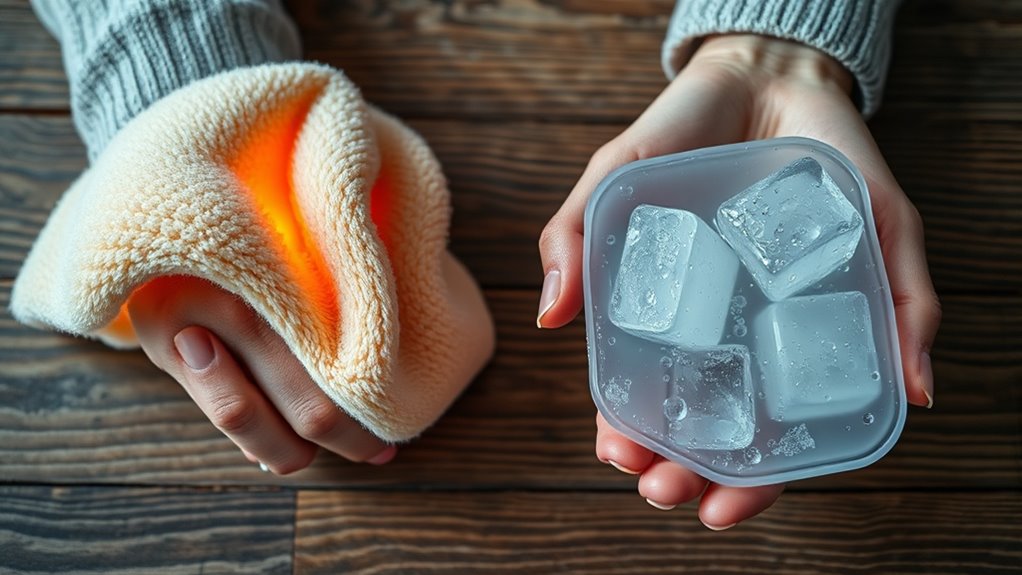
For arthritis pain, you should use heat therapy to relax muscles, increase blood flow, and reduce stiffness, especially before activity or to ease chronic discomfort. Cold therapy works best for recent injuries or flare-ups, as it diminishes swelling, numbs sharp pain, and reduces inflammation. Knowing when to apply each type can make a big difference in your relief. Continuing will give you more tips on how to safely and effectively use these therapies.
Key Takeaways
- Heat therapy relaxes muscles, increases blood flow, and alleviates stiffness, making it ideal for chronic pain and muscle tension.
- Cold therapy reduces inflammation, swelling, and numbs sharp pain, suitable for recent injuries and flare-ups.
- Use heat before activity to loosen joints, and cold after activity to minimize inflammation and swelling.
- Limit treatment times to prevent skin damage; avoid heat on broken skin and cold if sensation is impaired.
- Alternating heat and cold can provide comprehensive relief by addressing both muscle tension and inflammation.
How Heat Therapy Alleviates Arthritis Discomfort
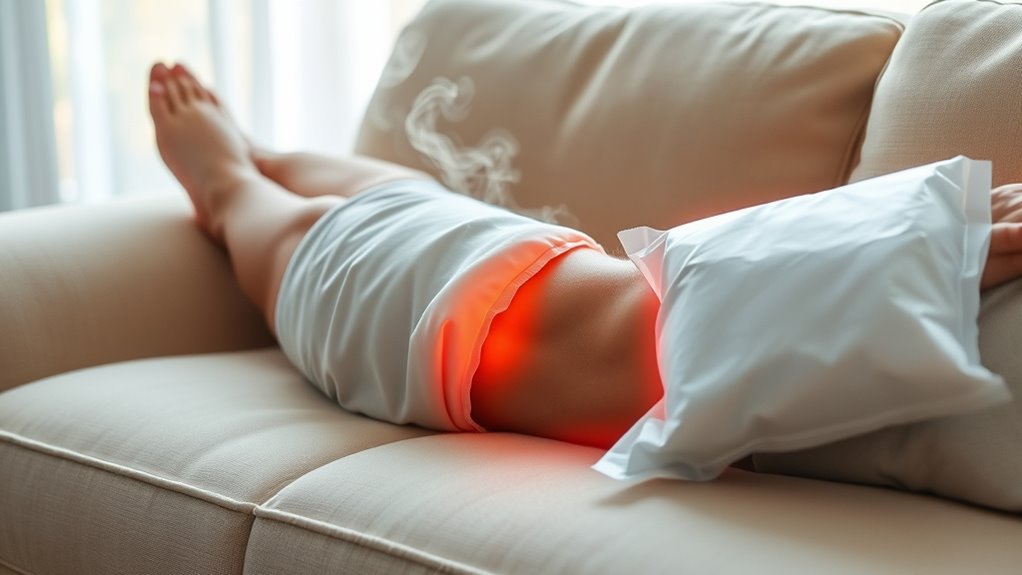

Heat therapy works by increasing blood flow to affected joints, which helps reduce stiffness and relieve pain associated with arthritis. When you apply heat, your blood vessels expand, allowing more oxygen and nutrients to reach the damaged tissues. This process accelerates healing and relaxes tense muscles around the joint, making movement easier. Heat also helps break down joint stiffness by soothing sore muscles and reducing muscle spasms. You might notice decreased pain and improved flexibility after regular heat application. Additionally, using contrast therapy, which involves alternating between heat and cold, can further enhance recovery and reduce inflammation. Incorporating evidence-based techniques can optimize treatment outcomes. Understanding the importance of proper timing ensures heat therapy is used safely and effectively. Remember, heat therapy is best for chronic pain or stiffness, but avoid using it during active inflammation or swelling.
The Role of Cold Therapy in Reducing Inflammation

Cold therapy is an effective way to reduce inflammation and numb pain in affected areas. When you apply cold, it constricts blood vessels, which helps decrease swelling and limits inflammatory responses. This can bring quick relief during flare-ups. To visualize, imagine:
- A cold pack pressed against your swollen joint, cooling the area rapidly.
- The skin turning slightly red then pale as blood flow slows.
- A soothing numbness spreading, dulling sharp pain.
When to Use Heat Versus Cold Treatments
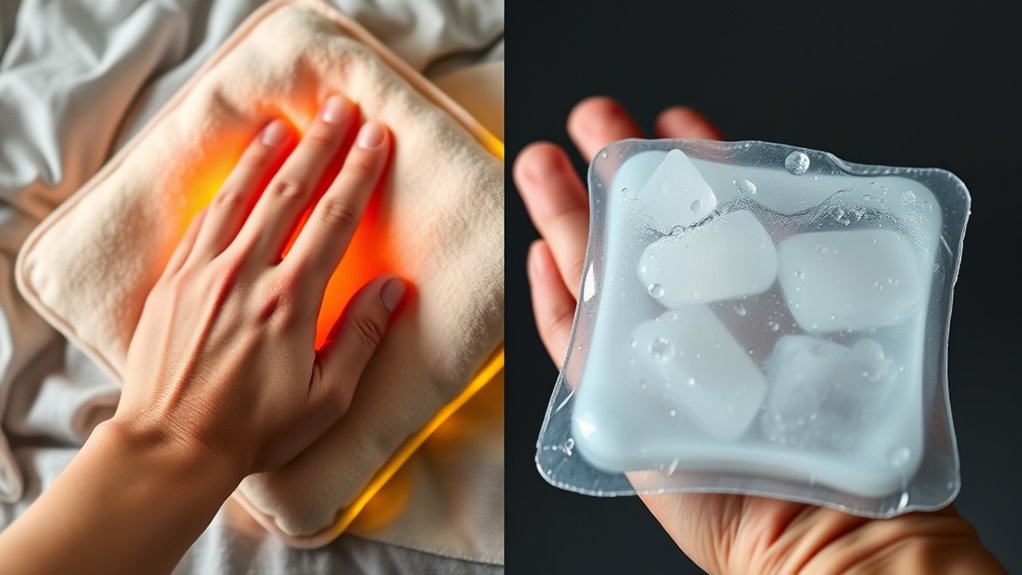

Understanding when to use heat versus cold treatments depends on the nature of your injury or condition. If you’re dealing with stiffness, muscle tension, or chronic pain, heat can help relax muscles and improve blood flow. Apply heat before activity to ease movement or after to soothe tight muscles. Conversely, cold treatments are best for recent injuries or inflammation. If you notice swelling, redness, or sharp pain, using cold can reduce swelling and numb pain. Cold is especially effective within the first 48 hours of an injury. Knowing these differences allows you to choose the appropriate therapy for your symptoms, promoting healing and comfort. Proper application techniques can enhance the effectiveness of either therapy and prevent skin damage. Additionally, staying informed about AI in Business can provide insights into innovative health tech solutions that may enhance treatment options in the future. Incorporating evidence-based practices ensures you are using the most effective methods for managing your arthritis pain. Recognizing appropriate timing for heat or cold application is crucial to maximize benefits and avoid potential adverse effects.
Precautions and Risks of Thermal Therapies

While thermal therapies can provide effective relief, they also carry potential risks if not used properly. You need to be cautious to prevent injuries or worsening pain. Here are some key precautions:
Thermal therapies offer relief but require caution to prevent injuries and worsening pain.
- Avoid applying heat or cold directly to broken or irritated skin to prevent burns or frostbite.
- Limit treatment time to 15-20 minutes to reduce the risk of skin damage or nerve issues.
- Never use thermal devices if you have impaired sensation, poor circulation, or skin infections, as you may not feel if damage occurs.
- Always ensure you use appropriate safety measures and proper techniques when applying thermal therapies to avoid inadvertent harm.
- Be aware that improper use of exfoliating acids can increase skin sensitivity, so caution is advised when using combined treatments.
Always follow manufacturer instructions and consult your healthcare provider if you’re unsure about safe usage. Proper precautions guarantee you get relief without risking harm.
Combining Heat and Cold for Optimal Relief
Combining heat and cold therapies can enhance pain relief and speed up recovery when used correctly. Alternating between heat and cold can target different aspects of arthritis pain. Use heat to relax tense muscles and improve blood flow, easing stiffness. Cold therapy reduces inflammation and numbs sharp pain. Start with heat for 15-20 minutes, then switch to cold for 10-15 minutes, allowing your skin to recover between applications. This method can reduce swelling, improve flexibility, and provide more all-encompassing relief. Incorporating the appropriate juice cleansing techniques can also support overall wellness and aid in inflammation reduction, complementing your therapy. Always listen to your body and avoid overdoing it. If you experience increased pain or discomfort, stop treatments and consult your healthcare provider. Combining these therapies thoughtfully can maximize benefits and help you manage arthritis symptoms more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Thermal Therapies Replace Medication for Arthritis Pain?
You wonder if thermal therapies can replace medication for arthritis pain. While they can provide significant relief, they typically aren’t enough on their own for everyone. Thermal treatments like heat and cold can ease discomfort and reduce inflammation, but they usually work best alongside medications or other therapies. Talk to your healthcare provider to create an all-encompassing pain management plan tailored to your needs, rather than relying solely on thermal therapies.
Are There Specific Arthritis Types That Respond Better to Heat or Cold?
Think of your arthritis like a garden—each type needs different care. You might find that osteoarthritis responds well to heat, easing stiffness and relaxing muscles. In contrast, cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain in rheumatoid arthritis. You should pay attention to how your body reacts, as some types respond better to specific treatments. Experiment carefully, and always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
How Long Should Each Heat or Cold Session Last?
You should aim for 15 to 20-minute sessions when applying heat or cold. For heat, guarantee the temperature is warm but not scalding to avoid burns, and take breaks if you feel uncomfortable. Cold packs should be wrapped in a cloth and used for similar durations to reduce swelling and numb pain. Always listen to your body, and consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Can Children or Seniors Safely Use Thermal Therapies for Arthritis?
Like a gentle breeze on a warm day, thermal therapies can bring relief, but safety matters. Children and seniors can use heat or cold treatments, yet you should always consult a healthcare professional first. They’re more sensitive, so proper application and duration are essential. Never apply heat or cold directly to the skin, and watch for any adverse reactions. Your best bet is to follow expert advice to keep everyone safe and comfortable.
Are There Any Long-Term Effects of Frequent Thermal Therapy Use?
You might wonder if frequent thermal therapy has long-term effects. While occasional use is generally safe, overusing heat or cold can cause skin irritation, nerve damage, or decreased sensation. If you regularly rely on these therapies, you could risk tissue damage or altered nerve responses. To stay safe, follow recommended durations and consult a healthcare professional if you notice any adverse effects, ensuring your treatment remains beneficial.
Conclusion
Just like a skilled artist chooses the right brush for each stroke, knowing when to apply heat or cold can transform your arthritis relief. By understanding their roles, you can create your own masterpiece of comfort—soothing inflammation like a gentle wave or calming pain like a quiet winter’s night. With mindful use, you hold the palette to ease your discomfort, turning everyday struggles into moments of relief and renewed movement.









