Interested in learning more about how our Certified Aging in Place Specialist (CAPS) professionals can modify homes to accommodate the changing needs of seniors?
Our team's wealth of knowledge and experience in construction, architecture, and design is unparalleled.
With a focus on enhancing accessibility and safety, they tailor solutions to promote independence for aging individuals.
Stay tuned to discover how our CAPS professionals are revolutionizing the concept of aging in place and improving the quality of life for seniors across the board.
Key Takeaways
- Over 25 years of expertise in barrier-free living solutions for seniors.
- Specialization in tailored home modifications promoting independence and quality of life.
- Dedicated to enhancing safety, accessibility, and comfort for aging in place.
- Providing compassionate, personalized solutions for unique needs of older adults.
Meet Our CAPS Certified Specialists
With over 25 years of industry experience, our CAPS certified specialists are dedicated to creating barrier-free living solutions for seniors. As aging in place specialists, we understand the unique needs of older individuals who wish to remain in their homes comfortably and safely.
Our team excels in residential remodeling and modifications tailored to meet individual needs, ensuring that each home isn't just a house but a sanctuary for aging gracefully. We bring a wealth of skills and expertise to every project, guaranteeing that our clients receive the best in accessible design and construction.
By focusing on the specific requirements of seniors, we transform houses into homes that promote independence and well-being. Whether it's adding grab bars, widening doorways, or installing ramps, our commitment to enhancing the quality of life for older adults shines through in all our residential projects.
Trust our CAPS certified specialists to make your home a place where you can age with dignity and comfort.
Expertise in Home Modifications and Design

Our dedication to creating barrier-free living solutions for seniors extends to our expertise in home modifications and design, where we specialize in enhancing safety and accessibility through tailored solutions.
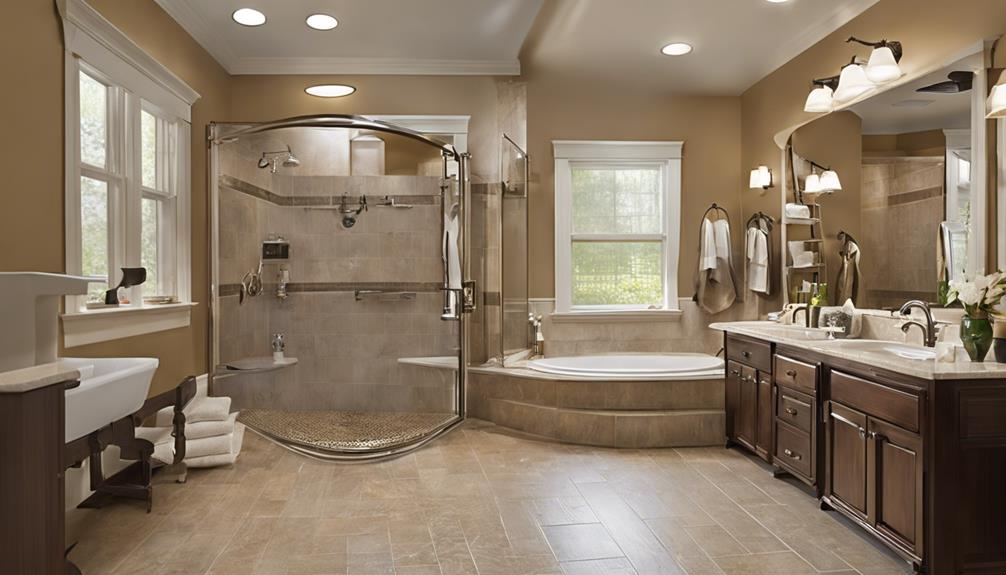
As Aging in Place Specialists, we understand the importance of making homes not just livable, but also safe and accommodating for individuals as they age. Our focus on home modifications includes widening doorways, modifying showers for easier access, installing grab bars in strategic locations, and adjusting countertop heights to ensure daily living tasks are manageable.
We excel in creating wheelchair-friendly spaces, ensuring shower accessibility, and implementing handrails and grab bars where needed. Our compassionate approach drives us to provide comprehensive services beyond just physical modifications; we also offer support with hoarding cleanup, organization, and real estate guidance tailored to older adults' unique needs.
When it comes to home safety, accessibility, and design solutions, our expertise is unmatched in promoting independence and enhancing quality of life for seniors.
Promoting Independence and Quality of Life
How can tailored home modifications enhance independence and quality of life for seniors? As CAPS specialists, we understand the importance of creating living spaces that support seniors in maintaining their autonomy and well-being. Here's how our expertise in tailored home modifications promotes independence and quality of life for seniors:
- Familiar Surroundings: By making adjustments to the existing home environment, we help seniors stay in the place they know and love, reducing the stress and costs associated with relocating.
- Safety and Accessibility: Addressing physical changes that come with aging, we ensure that the living space is safe and easy to navigate, promoting independence and peace of mind.
- Aging in Place: Our modifications support the concept of aging in place, allowing seniors to live comfortably in their own homes for as long as possible.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Through promoting independence and creating a safe environment, we empower seniors to enjoy a higher quality of life, filled with dignity and comfort.
Tailored Solutions for Unique Needs
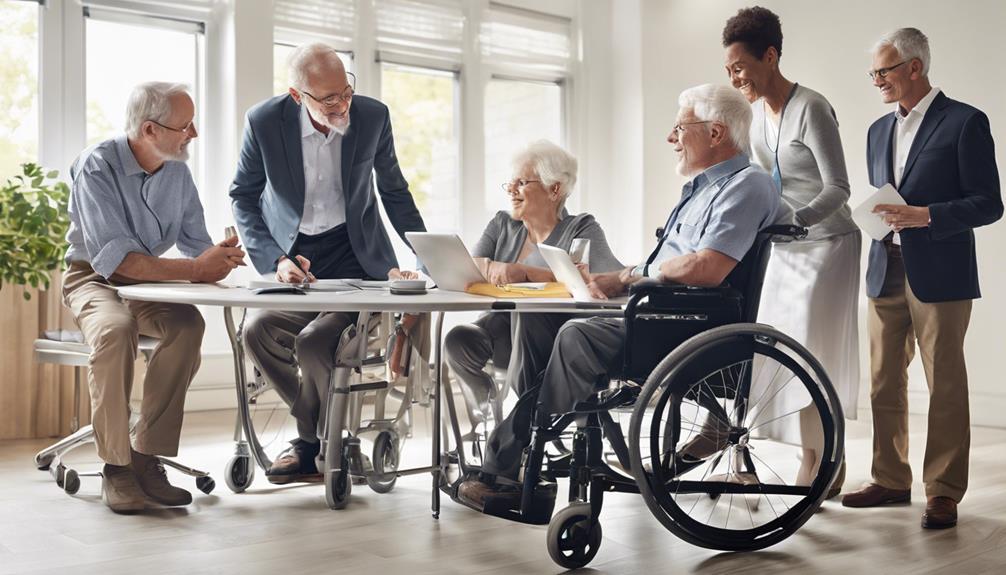

Tailored to meet the unique needs of older adults, our CAPS experts specialize in providing personalized home modifications for aging in place. We understand that each individual has specific requirements to maintain their independence and safety at home. Our team excels in creating customized solutions that enhance accessibility and ensure a secure living environment for older adults. From widening doorways to installing grab bars and improving lighting, our modifications are designed to cater to diverse care plans and evolving needs. Here is a glimpse of the tailored solutions our CAPS experts offer:
| Home Modifications | Care Plans | Living Spaces |
|---|---|---|
| Widening Doorways | Wheelchair Accommodation | Adapting Furniture Layout |
| Modifying Showers | Shower Accessibility | Ramps Installation |
| Adding Grab Bars | Grab Bars Installation | Countertop Adjustments |
| Improving Lighting | Handrails Addition | Furniture Rearrangement |
| Creating Ramps | Countertop Adjustments | Lighting Enhancements |
At CAPS, we are dedicated to ensuring that older adults can age in place comfortably and safely through our tailored solutions and expert care.
Dedicated to Aging in Place Solutions
Meeting the evolving needs of older adults, we're committed to providing dedicated solutions for aging in place that prioritize comfort, safety, and independence. As Certified Aging in Place Specialists (CAPS), our expertise lies in tailoring home modifications to cater to the unique requirements of each individual.
Here is how we address aging in place solutions:
- Tailored Modifications: We specialize in widening doorways, modifying showers, adding grab bars, and enhancing lighting to ensure accessibility and safety within homes.
- Adapting Living Spaces: Our CAPS professionals excel in creating ramps, rearranging furniture, and making other adjustments to accommodate changing needs seamlessly.
- Comprehensive Services: Beyond physical modifications, we offer services such as wheelchair accommodation, shower accessibility enhancements, grab bars installation, handrails, and countertop adjustments.
- Holistic Support: CAPS specialists go beyond traditional modifications, providing assistance with hoarding cleanup, organization, trash removal, and real estate guidance to create a holistic aging in place solution.
For us, being customer service skills essential to ensure that every aspect of aging in place is addressed with care and expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Certified Aging in Place Specialist Job Description?
We assess individual needs, recommend modifications, and execute projects with precision. Our focus is on enhancing safety and mobility in seniors' homes through features like grab bars, ramps, and wider doorways.
We work across industries like construction, architecture, and design to help seniors maintain independence and address physical and cognitive changes. Our goal is to reduce relocation stress and create comfortable living spaces for aging in place.
Conclusion
As CAPS certified specialists, we're dedicated to creating homes that not only accommodate the needs of aging individuals but also promote independence and enhance quality of life.
Remember, 'Home is where the heart is.' Let's help you create a safe and comfortable environment where you can age gracefully and enjoy the comforts of home for years to come.
Trust our expertise in home modifications and design to support you on your aging-in-place journey.