Navigating the realm of joint health can often feel like wading through a dense forest when trying to differentiate between arthrosis and arthritis.
Both conditions present challenges, yet understanding their distinct nature is key to choosing the right direction for effective management.
Let's explore the intricate nuances of these joint disorders, unraveling their origins, symptoms, and treatment options to shed light on the best way forward for those grappling with joint discomfort.
Key Takeaways
- Arthrosis: Bone-to-bone rubbing, stiffness, bone spur formation.
- Arthritis: Joint inflammation, fatigue, joint deformities.
- Early recognition crucial for effective management.
- Treatment includes medication, physical therapy, surgery options.
Symptoms of Arthritis Vs Arthrosis
Comparing the symptoms of arthritis to arthrosis reveals distinct differences in the manifestations experienced by individuals with these joint conditions. Arthritis commonly presents with redness, swelling, warmth in affected joints, along with joint inflammation and skin involvement. In contrast, arthrosis symptoms typically involve joint pain, stiffness, reduced flexibility, bone-to-bone rubbing, and bone spur formation due to cartilage breakdown.
While arthritis may cause fatigue, fever, and achy pain in joints, these aren't typically associated with arthrosis. Furthermore, arthritis can lead to joint deformities, whereas arthrosis results in painful bone-to-bone contact. Both conditions share symptoms like decreased range of motion, tenderness around affected joints, and swelling, but they may differ in specific characteristics. Understanding these differences is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of individuals suffering from arthritis or arthrosis.
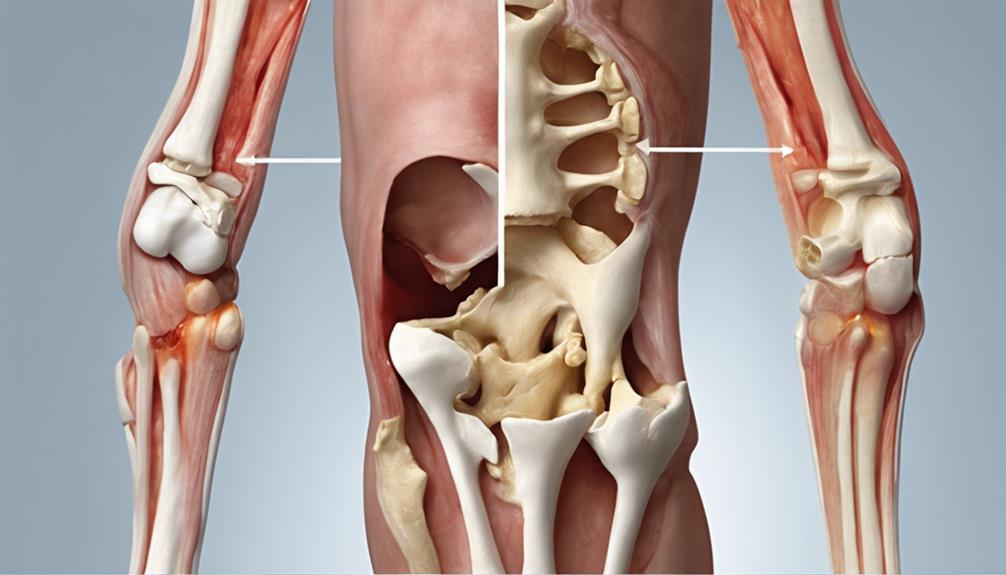
Joints Affected by Arthrosis
Moving from the symptoms of arthritis and arthrosis to the specific joints affected by arthrosis, it's crucial to understand the common areas where this degenerative joint condition tends to manifest. Arthrosis commonly targets joints such as the knees, hips, hands, and neck. Among these, weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips are most frequently affected by arthrosis.
The constant stress and repetitive use these joints endure over time contribute to the gradual breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain and reduced mobility. In the hands, arthrosis can cause discomfort and limitation in movement, impacting daily activities. Additionally, arthrosis in the neck can result in stiffness and a restricted range of motion, affecting the ability to turn or tilt the head comfortably.
Understanding the joints susceptible to arthrosis is essential in recognizing early symptoms and seeking appropriate care to manage the condition effectively.
Causes of Arthritis and Arthrosis
Injuries, infections, metabolic disorders, and immune system abnormalities are known factors that can contribute to the development of both arthritis and arthrosis. Arthritis can be triggered by joint injuries, infections, and metabolic disorders, leading to inflammation and pain in the joints.
On the other hand, arthrosis is commonly associated with aging and wear-and-tear on cartilage, gradually deteriorating the joint structures. Weight problems can exacerbate symptoms of both arthritis and arthrosis, putting additional strain on the affected joints.
In cases of certain types of arthritis, immune system disorders play a significant role in the onset of the condition, causing the immune system to mistakenly attack healthy joint tissues. Understanding these causes is crucial in managing and potentially preventing the progression of arthritis and arthrosis.
Diagnosing Arthritis
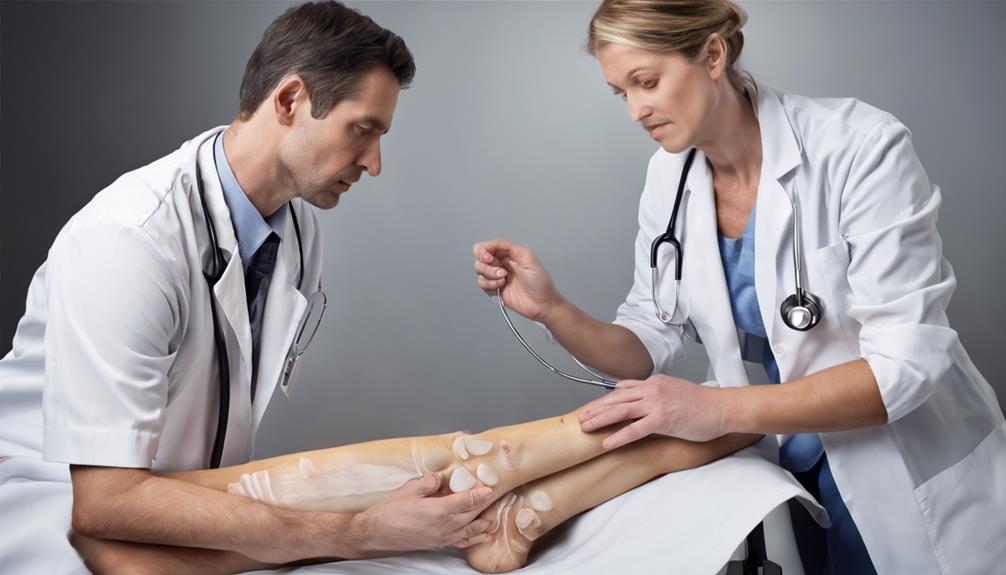
When diagnosing arthritis, healthcare providers typically evaluate symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, and stiffness to determine the presence and severity of the condition. These symptoms are key indicators of joint inflammation, a hallmark of various types of arthritis, including arthrosis.
To confirm a diagnosis, healthcare professionals may order blood tests to check for inflammation markers like C-reactive protein or rheumatoid factor. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasound can provide detailed images of the joints, aiding in the identification of arthritis-related changes.
In some cases, joint aspiration, a procedure involving the removal of fluid from the affected joint, may be necessary to diagnose specific types of arthritis accurately. Additionally, understanding one's family history is crucial in the diagnostic process as it helps uncover genetic predispositions and potential risk factors for developing arthritis.
Treatment Strategies for Arthritis
In addressing arthritis, a multifaceted approach encompassing medication, physical therapy, occupational therapy, steroid injections, and surgery is often employed to effectively manage the condition and enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by it.
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help alleviate symptoms and slow down joint damage.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises and stretches can improve joint flexibility, strength, and function.
- Surgery: Procedures like joint fusion or joint replacement may be recommended for severe cases to restore mobility and reduce pain.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Customized care plans that consider the individual's specific arthritis type, severity, and lifestyle are essential for optimal management and outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Treat Arthrosis?
When treating arthrosis, we focus on managing symptoms, slowing cartilage breakdown, and maintaining joint function. Physical therapy, medications like NSAIDs, and lifestyle adjustments play crucial roles.
Strengthening muscles around affected joints, managing weight, and protecting joints are key strategies. In severe cases, surgery such as joint replacement may be necessary.
It's important to address pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall quality of life for individuals with arthrosis.
What Is the Medical Term Arthrosis?
The medical term for arthrosis is osteoarthritis. It's a condition involving joint degeneration due to cartilage wear, leading to bone friction.
Osteoarthritis typically affects weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, hands, and neck. Symptoms may include pain, stiffness, swelling, and limited range of motion.
Treatment aims to manage symptoms, slow down joint deterioration, and enhance quality of life. It's crucial to seek medical advice for proper management and care.
What Are the Levels of Arthrosis?
We can break down arthrosis into levels to gauge the extent of joint damage. These levels range from mild, where cartilage shows early signs of wear, to moderate, with more noticeable deterioration, and severe, where significant cartilage damage occurs.
Understanding these stages helps tailor treatment plans, ensuring appropriate care. In severe cases, interventions may include surgical options. Tracking the progression of arthrosis through these levels is crucial for effective management.
How Is Arthrosis Different From Arthritis?
When comparing arthrosis and arthritis, the key distinction lies in their underlying causes and specific characteristics. Arthrosis is primarily a result of cartilage breakdown due to wear and tear, affecting weight-bearing joints predominantly.
On the other hand, arthritis is a broader term encompassing various joint inflammation conditions, including degenerative joint disease like arthrosis and autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout.
Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the differences between arthrosis and arthritis is like deciphering a complex puzzle with distinct pieces. Understanding these conditions allows us to tailor treatment plans and provide relief for those struggling with joint pain.
Just like a skilled puzzle solver, we can piece together the right strategies to help individuals improve their quality of life and find comfort amidst the challenges of these joint conditions.