During a recent routine examination, we observed a patient with a unique fold in their earlobe, which led us to investigate the intriguing link between this physical trait and the possible risk of heart disease.
As we delved into the research, we uncovered compelling evidence suggesting that the earlobe crease could serve as a subtle yet significant indicator of underlying coronary artery disease.
The implications of this association are profound, raising questions about early detection, preventative measures, and the potential for improving cardiovascular health outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Diagonal earlobe crease (DELC) linked to increased CAD risk.
- DELC may indicate altered atherosclerosis-related proteins and hormones.
- Recognizing DELC as a marker for underlying atherosclerosis.
- Understanding biochemical pathways for preventive measures against heart disease.
Understanding the Earlobe Crease Connection
In exploring the potential link between earlobe creases and heart disease, researchers have identified a notable association known as the diagonal earlobe crease (DELC), also recognized as Frank's sign. This distinctive mark, when present, has been linked to an increased risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) and heart attacks. The connection between earlobe creases and cardiovascular risk factors like atherosclerosis is intriguing. Studies suggest that individuals with this earlobe crease may have alterations in atherosclerosis-related proteins and hormones, potentially contributing to the development and progression of CAD.
Understanding the earlobe crease connection is crucial in the realm of CAD management. Recognizing the significance of DELC as a potential marker for underlying atherosclerosis can aid in identifying individuals at higher risk for heart-related issues. By delving into the mechanisms behind this association, healthcare providers can tailor interventions and treatments more effectively, focusing on mitigating risks associated with atherosclerosis in individuals with earlobe creases. This knowledge underscores the importance of early detection and management of cardiovascular risk factors to promote heart health.
Mechanisms Behind the Heart Disease Link
Exploring the intricate biochemical pathways underlying the correlation between earlobe creases and coronary artery disease reveals compelling insights into the mechanisms driving this association. Studies suggest that deficiencies in proteins like adropin and irisin may contribute to the development of atherosclerosis in individuals with earlobe creases. Additionally, low serum levels of the age-suppressing hormone Klotho have been observed in individuals with both earlobe creases and coronary artery disease (CAD). The altered levels of these key proteins and hormones in affected individuals indicate a potential link between earlobe creases and CAD. People with diagonal earlobe creases and CAD display distinct biochemical profiles, highlighting possible pathophysiological links between the two conditions. Understanding these mechanisms can provide valuable insights for developing preventive measures and targeted treatment strategies for individuals at risk of heart disease.
| Proteins | Hormones | Pathophysiological Links | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adropin, Irisin | Klotho | Atherosclerosis | Lifestyle changes |
Risk Assessment and Prevention Strategies
Assessing the risk factors associated with diagonal earlobe crease (DELC) can aid in formulating effective prevention strategies for coronary artery disease (CAD). Individuals with DELC, in conjunction with risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and high BMI, face an elevated risk of developing ischemic heart disease (IHD).
Early detection of DELC during clinical examinations plays a pivotal role in enabling timely intervention and management strategies to prevent complications related to IHD. Notably, the presence of DELC, combined with other cardiovascular risk factors, has shown a significant association with IHD in various study populations, underscoring its potential as a predictive marker.
Therefore, proper cardiovascular risk assessment and control of associated factors like hypertension are imperative in the prevention and management of ischemic heart disease in individuals exhibiting diagonal earlobe creases. By implementing targeted preventive strategies based on risk assessment findings, healthcare providers can work towards reducing the burden of CAD and enhancing heart health outcomes for at-risk individuals.
Famous Cases of Earlobe Crease Sign
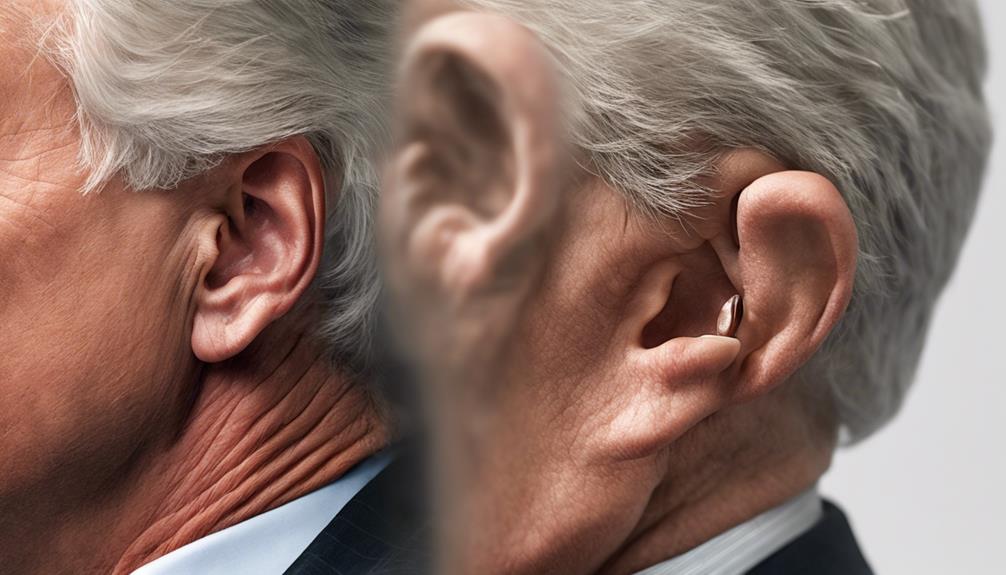
Notable individuals such as Steven Spielberg and George W. Bush have been identified as having the diagonal earlobe crease (DELC), adding to the intriguing connection between this physical trait and heart health. The association between ear creases and heart attacks has been observed in patients under 60 with chest pain and coronary artery blockages, suggesting a potential link between these two seemingly unrelated factors. The vulnerability of end-arteries supplying the heart and ears to damage may contribute to this connection. One proposed theory involves the loss of elastin and elastic fibers, akin to coronary artery disease (CAD), as a possible explanation for the relationship. Genetic factors are also believed to play a significant role in this association across different ethnic populations.
| Notable Individuals | Physical Trait | Heart Health |
|---|---|---|
| Steven Spielberg | DELC | Heart Attacks |
| George W. Bush | DELC | Coronary Artery Blockages |
Diagnostic Value and Research Findings
The correlation between the presence of diagonal earlobe crease (DELC) and heightened mortality risk has been extensively documented in research studies. DELC isn't only associated with coronary artery disease (CAD) but also considered a predictive factor for atherosclerotic disease.
Studies have delved into the diagnostic accuracy of DELC in identifying chronic coronary syndromes, revealing varying sensitivity and specificity results. This earlobe crease can serve as a specific sign warranting further assessment in individuals with morbilliform eruptions.
Understanding the connection between visible age-related signs such as earlobe creases and heart health may play a crucial role in the early detection and prevention of heart disease. By recognizing DELC as one of the risk factors linked to CAD, healthcare providers can potentially leverage this physical characteristic to improve diagnostic strategies and enhance patient outcomes through proactive interventions and tailored treatment plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a Crease in the Earlobe a Sign of Heart Disease?
Yes, a crease in the earlobe can potentially be a sign of heart disease. Research indicates that a diagonal earlobe crease (DELC) has been associated with an increased risk of coronary artery disease (CAD).
Studies suggest that DELC may serve as an independent marker for CAD and could predict adverse cardiovascular events. Early recognition of DELC by healthcare providers may assist in the timely diagnosis and management of heart disease.
How Accurate Is the Frank's Sign?
When evaluating the accuracy of Frank's sign, it's crucial to consider its predictive value and consistency across various populations. Research indicates a potential link between this earlobe crease and coronary artery disease risk factors.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms behind this association is key to determining the reliability of Frank's sign as a visible marker for cardiovascular health. Analyzing its predictive power and broader implications can provide valuable insights into its clinical significance.
How Long Can Someone With CAD Live?
We can expect individuals with CAD to live for many years with proper management. Factors like the extent of coronary artery blockages, overall health, and response to treatment influence prognosis.
Lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and regular follow-up care significantly enhance longevity and quality of life for CAD patients. Advances in therapies, interventions, and rehabilitation programs have improved survival rates.
Early detection, timely interventions, and monitoring are vital for maximizing life expectancy and reducing complications in CAD patients.
What Is the Life Expectancy of Someone With Atherosclerosis?
We can estimate the life expectancy of someone with atherosclerosis by considering factors such as the extent of plaque buildup, lifestyle choices, and medical interventions.
Atherosclerosis, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications like heart attacks and strokes, impacting life expectancy.
However, with proper management through medications, lifestyle modifications, and timely interventions, individuals can improve their prognosis and potentially extend their life expectancy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the presence of Earlobe Crease Heart Disease serves as a valuable indicator for underlying coronary artery disease. Like a compass pointing north, recognizing this subtle sign can guide clinicians towards early diagnosis and intervention, potentially saving lives.
Further research into the mechanisms behind this link is crucial for improving risk assessment and prevention strategies in the fight against atherosclerotic disease.