Choosing between hydraulic and electric patient lifts depends on safety features and your control. Electric lifts are easier to operate and respond smoothly, reducing effort and preventing operator fatigue, but they rely on batteries that can fail. Hydraulic lifts offer reliable manual control but may require more strength and skill. Proper maintenance and training are essential for both. To find out which lift suits your needs best, explore the detailed points ahead.
Key Takeaways
- Both lifts include safety features like emergency stops and overload protection, but proper training is essential for safe operation.
- Electric lifts offer smoother, more controlled transfers with less physical effort, reducing operator error risks.
- Hydraulic lifts depend on manual pumps, which may require more user skill and maintenance to prevent leaks and failures.
- Regular inspections and maintenance are critical for both types to prevent mechanical failures and ensure safety.
- Choosing the safer lift depends on proper use, maintenance, and operator training, not just the lift type itself.
How Do Hydraulic and Electric Patient Lifts Work and What Does That Mean for Safety?
Hydraulic and electric patient lifts operate differently, directly impacting safety during patient transfers. Hydraulic lifts use manual pumps or foot pedals to raise or lower patients, offering a smoother transfer that can enhance patient comfort. They tend to be more affordable upfront, making them a cost-effective choice for many facilities. Additionally, the type of lift can influence the safety protocols required during transfers, emphasizing the need for proper training and maintenance. Proper maintenance practices are essential to ensure all lifts operate safely and reliably over time. Electric lifts, on the other hand, rely on batteries and motors, providing effortless operation with minimal physical effort. This ease often translates into increased safety, reducing the risk of strain or injury during transfers. While electric lifts may have higher initial costs, their efficiency and user-friendliness can justify the investment, especially when considering patient comfort. Furthermore, understanding projector technology can help you appreciate the importance of reliable equipment and safety features in healthcare settings, ensuring optimal patient care. Selecting the appropriate lift involves considering factors such as patient weight capacity and ease of use to promote safety and comfort for both patients and caregivers.
What Are the Key Safety Features of Hydraulic and Electric Lifts?

Both hydraulic and electric patient lifts incorporate essential safety features designed to protect patients and caregivers during transfers. Their lift design focuses on stability, with wide bases and secure slings to prevent falls. Safety protocols often include overload protection systems that automatically stop the lift if weight limits are exceeded, ensuring safe handling. Emergency stop buttons are easily accessible, allowing quick halts if needed. Electric lifts typically have battery backup power, so transfers can proceed even during power outages, while hydraulic lifts rely on manual controls with safety valves to prevent sudden drops. Overall, these features help minimize risks, making both lift types reliable options when designed with safety in mind. Proper training and adherence to safety protocols further enhance their effectiveness. Understanding simple tools like BTU and CADR quick‑calculators can help evaluate and optimize the safety and efficiency of lift systems and related equipment. Additionally, considering power source reliability is crucial to ensure continuous operation during emergencies, and assessing safety feature integration can further enhance overall safety performance. Regular maintenance checks, including inspecting hydraulic and electrical components, are also vital to identify potential issues before they compromise safety.
What Risks and Challenges Are Associated With Each Lift Type?
Both hydraulic and electric lifts carry risks, such as mechanical failures that can compromise safety. Operator error is also a concern, especially if proper training isn’t provided. Understanding these challenges helps you take better precautions during patient transfers. Additionally, selecting energy-efficient equipment can reduce operational risks and support sustainable healthcare practices.
Mechanical Failure Risks
While hydraulic and electric patient lifts each have their advantages, they also come with specific mechanical failure risks that users should consider. Hydraulic lifts rely on fluid pressure, so hydraulic failure—such as leaks or broken seals—can lead to sudden drops or inability to lift. Hydraulic system failures may require specialized repairs to restore proper function. Electric lifts depend on batteries and electronic components; an electric malfunction, like a dead battery or motor failure, can immobilize the device. Both types require regular maintenance to prevent these issues. If neglected, mechanical failures can pose safety hazards during transfers, increasing the risk of injury. Being aware of these risks helps you perform routine inspections and maintenance, reducing the chances of unexpected failures and ensuring safer, more reliable lifts for patient transfers. Additionally, understanding device maintenance best practices can significantly extend the lifespan and safety of both lift types. Proper preventive care can also help identify early warning signs of potential failures, further enhancing safety. Moreover, adhering to manufacturer-recommended inspection procedures can help catch issues before they result in failure.
Operator Error Potential
Mechanical failures can be mitigated through regular maintenance, but operator errors often pose immediate safety risks during transfers. Poor user training or lack of proper training considerations increase these risks. Common mistakes include:
- Incorrect positioning of the patient or lift, risking falls or injuries
- Overloading the lift beyond its capacity, causing mechanical strain or failure
- Improper use of safety features, such as locking mechanisms or harnesses
Both hydraulic and electric lifts require thorough user training to minimize mistakes. Without proper training, you may misjudge patient weight, operate controls incorrectly, or overlook safety protocols. Ensuring staff are well-trained and familiar with each lift’s operation reduces operator error potential and enhances overall transfer safety. Proper training is essential for safe, effective patient handling with either lift type. Additionally, understanding nanotechnology advancements can lead to improved safety features and smarter assistive devices in the future, making patient transfer equipment more reliable and user-friendly.
How Stable and Controllable Are Hydraulic and Electric Lifts?
When it comes to stability during operation, both hydraulic and electric lifts have their strengths and weaknesses. You’ll find that ease of control varies between the two, affecting how smoothly and confidently you can maneuver patients. Response consistency is vital, so understanding how reliably each lift reacts to your commands can help you choose the right tool for your needs. Additionally, incorporating smart technology can enhance safety and efficiency in lift operation. For example, response accuracy is essential for ensuring patient safety and smooth handling during transfers. Proper lift maintenance also plays a crucial role in maintaining consistent performance over time. Incorporating connected equipment with sensors and monitoring systems can further improve operational reliability and safety. Regularly assessing performance stability helps ensure both lifts operate safely and effectively in various situations.
Stability During Operation
Hydraulic and electric patient lifts differ markedly in their stability and control during operation, affecting how confidently you can maneuver patients. Stability depends heavily on weight distribution and the lift’s center of gravity. Hydraulic lifts generally offer smoother adjustments, maintaining a stable center of gravity even when weight shifts. Electric lifts, however, can sometimes feel less stable if their weight isn’t evenly distributed or if the center of gravity isn’t properly balanced. To ensure safety, consider these points: 1. Properly position the patient to keep the center of gravity aligned with the lift’s base. 2. Regularly check the load’s weight distribution during lifts. 3. Use lifts with a low center of gravity for enhanced stability during movement. Additionally, understanding the hydrotherapy benefits can be helpful in selecting lifts that promote patient comfort and safety during transfers. Moreover, proper maintenance of the lifts can significantly impact their stability and overall safety performance. Regular inspection and correct operation procedures help maintain the stability of the equipment over time, especially when combined with knowledge of market options to choose the most reliable lifts.
Ease of Control
Ease of control is a key factor in how confidently you can operate hydraulic and electric patient lifts. Good lift ergonomics make handling safer and reduce fatigue, allowing you to maneuver lifts smoothly. Electric lifts often feature intuitive controls, making operation straightforward with minimal effort. Hydraulic lifts may require more manual input, which can be challenging if you’re not well-trained. Proper user training enhances your ability to control each lift confidently, ensuring safety for both patient and caregiver. Electric lifts typically offer finer control, giving you better precision during transfers. Hydraulic lifts, while reliable, may feel less responsive without adequate experience. Overall, the ease of control depends on the lift’s design and your familiarity with its operation, emphasizing the importance of proper training for safe and effective use. Additionally, lift ergonomics play a crucial role in ensuring comfort and safety during operation.
Response Consistency
Response consistency determines how reliably a lift maintains stability and control during transfers. With consistent response, your patient feels safer and more comfortable, reducing anxiety. Hydraulic lifts tend to offer steady, predictable movements, which enhance patient comfort during transfers. In contrast, electric lifts can sometimes respond unevenly, impacting control. When choosing between the two, consider these factors:
- Hydraulic lifts often provide smoother, more predictable responses.
- Electric lifts may experience slight delays or jerks, affecting stability.
- Cost considerations play a role, as hydraulic lifts typically require more maintenance for consistent performance.
Ultimately, response consistency influences both patient safety and comfort, helping you ensure smooth transfers with confidence.
How Easy Is It for Caregivers to Use Each Lift Type?
Caregivers often find that electric lifts are simpler to operate because they typically come with user-friendly controls and require less physical effort. This ease of use reduces strain and makes lifting safer for both caregiver and patient. Electric lifts often feature intuitive buttons or remote controls, so you spend less time learning complex procedures. When it comes to patient comfort, electric lifts allow for smoother, more controlled transfers, reducing discomfort. Cost considerations do play a role, as electric lifts tend to be more expensive upfront, but their ease of operation can lower training time and minimize injury risks. Hydraulic lifts, while reliable, often need more physical strength and manual effort, which can complicate use and compromise comfort. Overall, electric lifts tend to be more accessible for caregivers.
What Maintenance and Reliability Factors Keep Long-Term Safety in Check?
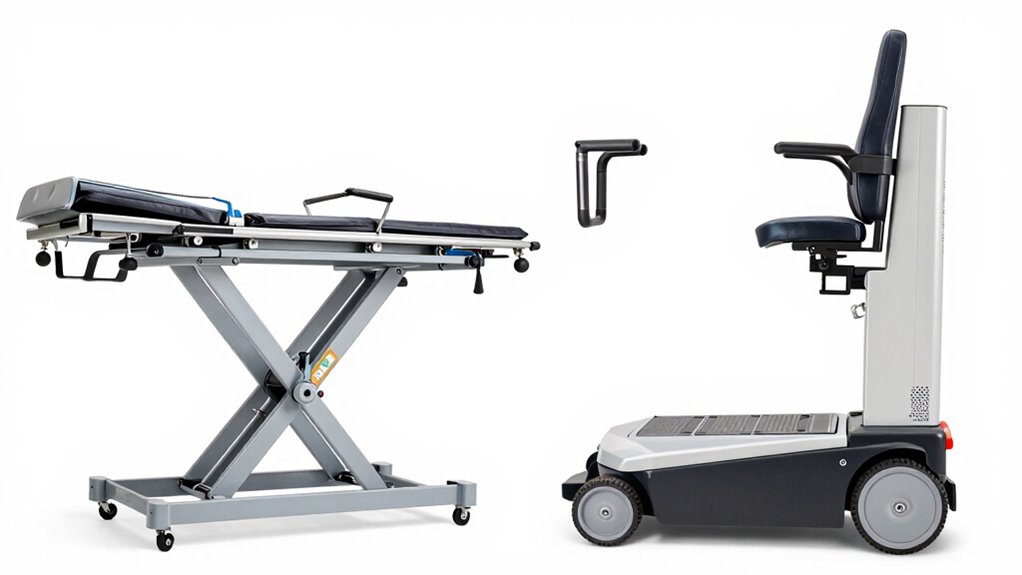

Maintaining the safety of patient lifts over time depends heavily on their ongoing reliability and proper upkeep. Regular maintenance protocols help identify issues early, preventing failures that could compromise safety. To ensure long-term dependability, focus on these key factors:
- Schedule routine inspections to catch wear and tear before problems develop.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance and parts replacement.
- Keep detailed records of maintenance activities to track reliability concerns over time.
Addressing these factors minimizes breakdowns and ensures your lift remains safe for patient transfers. Neglecting maintenance can lead to mechanical failures or malfunctions, increasing risks. Prioritizing consistent upkeep and understanding reliability concerns are essential for long-term safety and peace of mind.
How to Choose the Safer Patient Lift Based on Your Needs?
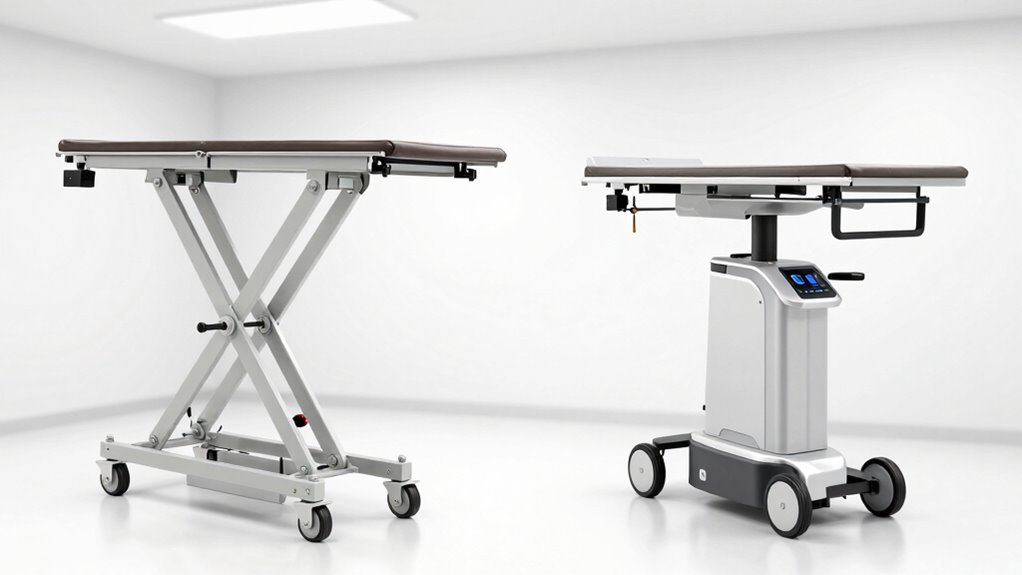

Choosing the right patient lift depends on your specific needs, environment, and patient requirements. To guarantee safety, consider factors like patient comfort and cost considerations. For example, electric lifts often provide smoother transfers, enhancing comfort for the patient, but may be pricier initially. Hydraulic lifts might be more affordable upfront but could require more maintenance. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Hydraulic Lift | Electric Lift | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Comfort | Moderate, depends on operation | High, smooth transfers | Patients needing gentle handling |
| Cost Considerations | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance | Budget-conscious facilities |
| Ease of Use | Manual effort required | Push-button operation | Caregivers seeking convenience |
Choosing wisely balances safety, comfort, and your budget.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Hydraulic or Electric Lifts More Cost-Effective Long-Term?
You’ll find that electric lifts tend to be more cost-effective long-term because their initial cost comparison is higher, but they usually have lower maintenance costs. Hydraulic lifts are often cheaper upfront, but you might spend more on repairs and upkeep over time. Electric lifts are easier to operate, which can reduce staff injury risk and associated costs, making them a smarter investment for ongoing safety and efficiency.
How Do Power Outages Affect Electric Lift Safety?
Imagine a quiet room suddenly plunged into darkness during a power outage, and your electric lift stops working. Power outage risks mean your electric lift may become unsafe if there’s no emergency backup. To guarantee safety, always have a manual override or backup plan in place. This way, you can confidently transfer patients even when the power’s out, reducing potential accidents and ensuring continuous care.
Can Hydraulic Lifts Handle Heavier Patients Better Than Electric?
Hydraulic lifts generally handle heavier patients better due to their higher weight capacity and robust lift stability. You’ll find they often support more weight safely, making them suitable for larger patients. Electric lifts may have lower weight limits, but hydraulic models are designed to provide steady, secure lifts even with heavier loads. So, if you need to lift heavier patients safely, hydraulic lifts are usually the better choice.
What Training Is Required for Proper Lift Operation?
To guarantee patient safety, you need proper staff training on lift operation. You should complete manufacturer-specific training sessions that cover safe handling, equipment checks, and emergency procedures. This training helps you understand the lift’s features, whether hydraulic or electric, and how to operate it correctly. Regular refreshers are essential to stay updated and maintain safety standards, ensuring both patients and staff are protected during transfers.
Are There Environmental Concerns With Either Lift Type?
You should consider environmental impact and sustainability concerns with both lift types. Hydraulic lifts use fluids that could leak and cause pollution, raising environmental impact issues. Electric lifts depend on batteries, which require proper disposal to prevent environmental harm. To minimize your environmental footprint, choose lifts with eco-friendly features, guarantee regular maintenance, and follow proper disposal procedures for batteries and fluids, promoting sustainability in patient care.
Conclusion
Choosing between hydraulic and electric patient lifts is like picking the right tool for a job—you want safety to be your guiding star. Both have their strengths and challenges, but understanding their features helps you navigate with confidence. Remember, the safest lift is the one that fits your needs and keeps both you and your patient secure. Trust your instincts and prioritize safety—after all, you’re the captain steering this essential journey.