As we get older, senile osteoporosis silently undermines our bone strength, acting like a sneaky foe.
As we explore the intricate mechanisms underlying this condition, we unravel a tapestry of factors influencing its onset and progression.
From the subtle changes in bone architecture to the clinical manifestations that often go unnoticed, the complexities of senile osteoporosis beckon us to delve deeper into its mysteries, shedding light on how we can better understand and manage this silent threat to our skeletal health.
Key Takeaways
- Hormonal shifts and reduced estrogen play a significant role.
- Exercise diversity crucial for bone health maintenance.
- Genetic predisposition and zinc deficiency are risk factors.
- Support groups and online resources aid in coping and education.
Causes of Senile Osteoporosis
Senile osteoporosis, a condition primarily caused by age-related bone loss and slower bone growth, significantly increases the susceptibility to fractures. Hormonal shifts, particularly in women, contribute to the development of senile osteoporosis. These shifts, such as reduced estrogen levels during menopause, can accelerate bone loss. Factors like body size, race, family history, diet, and lifestyle also play essential roles in the risk of developing this condition. For instance, individuals with a family history of osteoporosis or those with a diet lacking in calcium are at higher risk.
To maintain bone health and reduce the risk of senile osteoporosis, regular weight-bearing exercises are crucial. Exercises like walking, dancing, or weight training help improve bone density and strength. Understanding these causes of senile osteoporosis is vital for effective prevention and management strategies. By addressing these risk factors early on through lifestyle modifications, proper nutrition, and medical interventions when necessary, we can work towards reducing the prevalence and impact of this condition.
Symptoms and Signs
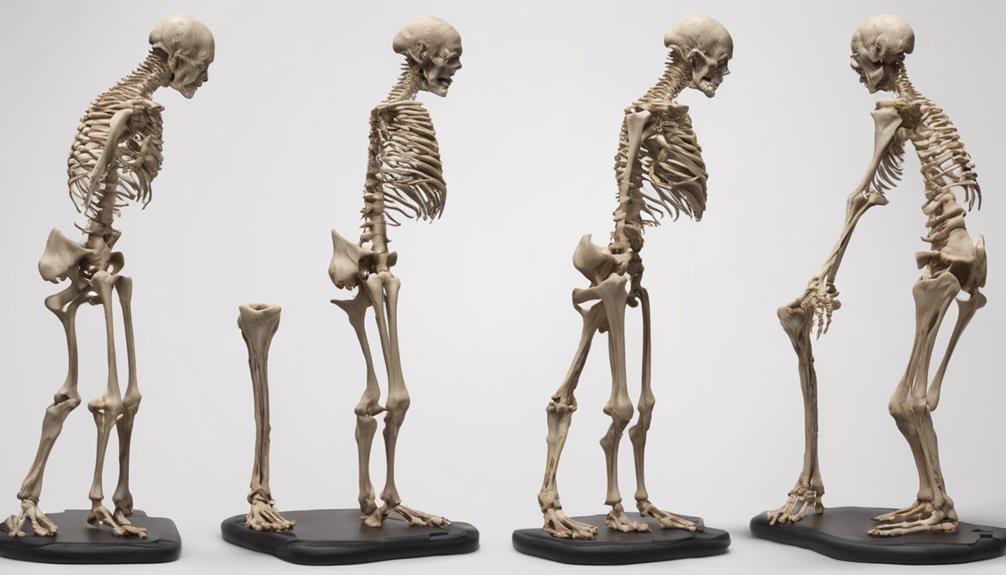
As bone mass decreases and fragility increases with age, individuals may start experiencing subtle changes that signal the onset of osteoporosis. Senile osteoporosis, characterized by progressive loss of bone mass, manifests through various symptoms and signs:
- Increased Risk of Fractures: Fragile bones in senile osteoporosis are more prone to fractures, even from minor incidents, leading to significant pain and immobility.
- Vertebral Fractures: Senile osteoporosis often results in vertebral fractures, causing severe back pain, height loss, and a hunched posture, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
- Chronic Symptoms: Symptoms of senile osteoporosis can be chronic and debilitating, affecting independence and overall health in older individuals. Managing these symptoms early on is crucial to prevent further bone deterioration and reduce the risk of fractures.
Proper intervention and care are essential to improve outcomes and enhance the well-being of individuals affected by senile osteoporosis.
Diagnostic Approaches
Utilizing a combination of advanced imaging techniques and clinical assessments, healthcare providers employ a comprehensive approach to diagnose and evaluate senile osteoporosis accurately.
Bone mineral density (BMD) measurements through dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) are crucial in identifying low bone mass and diagnosing osteoporosis in older individuals. The FRAX tool plays a vital role in estimating the 10-year probability of major osteoporotic fractures and hip fractures based on clinical risk factors, aiding in treatment decisions.
Blood tests measuring calcium, vitamin D levels, and bone turnover markers provide valuable information for diagnosing and assessing the severity of senile osteoporosis. Imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI help detect fractures, evaluate bone structure, and monitor disease progression in seniors.
Furthermore, clinical evaluation by healthcare providers, including assessing risk factors, medical history, physical examination, and symptom review, is essential for an accurate diagnosis of senile osteoporosis, ensuring appropriate management and care for affected individuals.
Risk Factors to Consider

Considering the multitude of factors that contribute to the risk of senile osteoporosis, it's imperative to acknowledge and address specific key elements that significantly impact bone health in older individuals.
When evaluating the risk of senile osteoporosis, it's crucial to consider:
- Age: As individuals age, the risk of developing osteoporosis increases due to natural bone density loss and decreased bone regeneration processes.
- Low Body Mass Index (BMI): Low BMI is associated with reduced bone density and an increased risk of fractures, making it a critical factor to consider in assessing osteoporosis risk.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition, including factors like race, age, body weight, and gender, can significantly influence an individual's susceptibility to senile osteoporosis.
These factors, coupled with zinc deficiency, inadequate calcium intake, poor vitamin D absorption, and peak bone mass levels, all play essential roles in determining bone density and overall bone health in aging individuals.
Treatment Options Available
Our approach to treating senile osteoporosis involves a combination of hormonal therapy, calcium supplementation, and vitamin D therapy to enhance bone formation and decrease bone resorption. Hormonal therapy helps maintain bone density by balancing hormone levels, reducing the risk of fractures in individuals with senile osteoporosis. Calcium supplementation is crucial as aging bodies may struggle to absorb enough calcium from diet alone, supporting bone strength and density. Vitamin D therapy aids in calcium absorption, promoting bone health and reducing fracture risk.
In addition to these foundational treatments, bisphosphonates are commonly prescribed to manage senile osteoporosis. These medications help to prevent bone loss, improve bone density, and reduce the risk of fractures in elderly individuals. Alongside pharmacological interventions, non-pharmacological approaches like modified diet and exercise play a vital role in treatment and prevention. Ensuring adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D3 is essential for supporting bone health and preventing further bone deterioration in individuals with senile osteoporosis.
Ongoing research into the anabolic effects of certain medications on bone offers promising avenues for future treatment options.
Importance of Nutrition

Exploring the role of nutrition in senile osteoporosis management reveals its crucial impact on preventing bone loss and promoting overall bone health. Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is essential for maintaining bone health in senile osteoporosis. Here's why nutrition is vital:
- Calcium-Rich Foods: Incorporating dark green vegetables, dairy products, and fish into the diet can help support bone density.
- Vitamin D Sources: Consuming fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods is beneficial for calcium absorption and bone strength.
- Supplements: Individuals who don't receive sufficient vitamin D through diet and sunlight exposure may require supplements to meet their needs.
A balanced diet, along with weight-bearing exercises and lifestyle modifications, plays a significant role in supporting bone health and reducing the risk of fractures in senile osteoporosis. By focusing on nutrition and ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining strong and healthy bones in their postmenopausal years.
Exercise Recommendations

Engage in regular weight-bearing exercises like walking, dancing, or weight lifting to enhance bone density and strength for individuals managing senile osteoporosis. These activities are crucial for improving bone health and reducing the risk of fractures in seniors. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises into your routine can help maintain muscle mass and bone strength. Balance exercises are also essential to prevent falls, which can lead to serious injuries in individuals with osteoporosis.
Consider incorporating high-impact exercises like jumping or running, as these activities stimulate bone formation and reduce bone loss in older adults with senile osteoporosis. Moreover, activities such as tai chi or yoga can enhance flexibility, posture, and overall bone health.
Following a well-rounded exercise program that includes aerobic, strength training, and balance exercises is recommended for seniors with osteoporosis to promote bone density, mobility, and independence. By prioritizing regular physical activity, individuals can take proactive steps to manage senile osteoporosis and improve their quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications
To optimize bone health and reduce the risk of fractures in individuals managing senile osteoporosis, incorporating lifestyle modifications such as regular weight-bearing exercises and a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is crucial. These changes aid in improving bone density, reducing the risk of fractures, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Here are three essential lifestyle modifications for individuals dealing with senile osteoporosis:
- Regular Weight-Bearing Exercises: Engaging in activities like walking, dancing, or stair climbing can help strengthen bones, improve balance, and reduce the risk of falls.
- Balanced Diet with Calcium and Vitamin D: Consuming foods high in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health, enhances calcium absorption, and reduces the likelihood of low bone mass and fractures.
- Preventive Measures to Avoid Falls: Using assistive devices, wearing appropriate footwear, and being cautious on slippery surfaces can significantly decrease the risk of falls and subsequent fractures.
Complications and Consequences

Senile osteoporosis poses significant risks of debilitating fractures in key areas of the body, such as the spine, hip, proximal humerus, and distal forearm. Vertebral fractures, a common consequence of this condition, can lead to severe back pain, height loss, and an increased risk of future fractures. Fragility fractures in senile osteoporosis are especially concerning as bones become more susceptible to breaking from minor incidents due to decreased bone mass and strength.
The chronic impact of bone mass loss in senile osteoporosis can manifest in various ways, affecting daily life and mobility. Over time, the progressive nature of this condition can result in a significant decrease in the quality of life for those affected, emphasizing the importance of early detection and management to mitigate the risk of these debilitating fractures.
It's crucial to address these complications to prevent further deterioration and enhance the overall well-being of individuals dealing with senile osteoporosis.
Prevention Strategies

In safeguarding against senile osteoporosis, prioritizing regular weight-bearing exercises remains a cornerstone in fortifying bone density and strength. Engaging in activities like walking, dancing, or weight training can make a significant impact on bone health. Additionally, ensuring an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D through a balanced diet or supplements is crucial for maintaining strong bones. Here are three essential strategies to prevent senile osteoporosis:
- Fall Prevention: Implement strategies such as keeping homes well-lit, decluttered, using handrails, and wearing appropriate footwear to reduce the risk of falls and fractures in seniors with osteoporosis.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Schedule routine check-ups, including bone density scans, to detect osteoporosis early, allowing for timely interventions that can improve outcomes and reduce complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Make positive changes like quitting smoking, moderating alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy weight to prevent senile osteoporosis and preserve bone health. These adjustments can have a significant impact on overall well-being and quality of life.
Support and Resources

We understand the importance of support and resources in managing senile osteoporosis. Support groups tailored for seniors provide a platform for sharing experiences and coping strategies.
Online osteoporosis resources offer valuable information on treatments and lifestyle adjustments for individuals dealing with this condition.
Support Groups for Seniors
Support groups for seniors with senile osteoporosis play a vital role in providing emotional support, education, and valuable resources for managing the condition effectively. These groups offer a sense of community and understanding among individuals facing similar challenges with bone health.
Participants can share experiences, coping strategies, and tips for improving bone strength and preventing falls. Support groups often organize educational sessions, guest speakers, and social activities to enhance overall well-being.
Joining a support group for senile osteoporosis can empower seniors to take control of their health and improve their quality of life. It's a safe space where individuals can find encouragement, information, and companionship on their journey towards better bone health.
Online Osteoporosis Resources
Navigating the realm of online osteoporosis resources opens a gateway to a wealth of support, information, and tools for individuals managing senile osteoporosis. These online resources provide access to educational materials, research articles, and valuable information to help understand and cope with senile osteoporosis.
Support groups and forums offer emotional support and a platform to connect and share experiences with others facing similar challenges. Websites dedicated to osteoporosis offer practical tips on lifestyle modifications, exercise routines, and nutritional guidance tailored to seniors.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Treat Severe Senile Osteoporosis?
We treat severe senile osteoporosis by combining pharmacological interventions like bisphosphonates to decrease bone resorption and improve density. Calcium and vitamin D3 supplementation are crucial for bone health.
Non-pharmacological methods include a calcium-rich diet and weight-bearing exercise. Our goal is to slow bone loss, improve strength, and reduce fracture risk.
Early intervention with medication, nutrition, and lifestyle changes is vital for effective management.
What Is the Life Expectancy of a Person With Osteoporosis?
We understand the concern about life expectancy in individuals with osteoporosis.
It's important to emphasize that timely diagnosis, proper management, and preventive measures can significantly impact longevity.
By prioritizing bone health through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring, we can reduce the risk of fractures and improve overall quality of life.
Taking proactive steps to address osteoporosis can lead to a longer, healthier, and more fulfilling life.
Can Vitamin D Reverse Osteoporosis?
Yes, vitamin D can potentially help reverse osteoporosis by supporting bone health and strength. Adequate levels of vitamin D are crucial for maintaining bone density and reducing the progression of osteoporosis, especially in older individuals.
Studies suggest that vitamin D supplementation can aid in preventing and treating osteoporosis by promoting bone mineralization and lowering fracture risk. Including vitamin D-rich foods in the diet or taking supplements under medical guidance may assist in managing osteoporosis effectively.
What Are the 5 Stages of Osteoporosis?
Sure!
The five stages of osteoporosis progress from normal bone density to severe bone weakness and complications. Beginning with optimal bone health, one moves through osteopenia, early, moderate, and advanced osteoporosis, where fracture risk increases significantly.
How can we best support individuals transitioning through these stages with compassion and evidence-based care? Let's explore ways to serve those affected by this condition with understanding and knowledge.
Conclusion
In conclusion, senile osteoporosis is a complex condition that requires attention and care. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their bone health.
Remember, 'an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.' With proper lifestyle modifications, support, and resources, we can work towards preventing fractures and maintaining strong bones as we age.
Let's prioritize our bone health for a brighter, healthier future.